What is procurement? Everything you need to know
Introduction to procurement
Procurement is the backbone of any organization, ensuring that businesses have the goods and services they need to operate smoothly and competitively. At its core, procurement involves the strategic selection and purchasing of materials, but it’s much more than simply buying goods. It’s about finding the right suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships to ensure value, quality, and reliability. With the advent of new technologies, the procurement landscape is rapidly evolving, making it an exciting area for innovation and efficiency improvements. This article will delve into the essentials of procurement, exploring its process, strategies, and the impact of technological advancements such as automation and artificial intelligence.

Download the 2024 Procurement Software Buyer’s Guide
Your guide to selecting the right procure-to-pay platform for your organization’s needs – to drive measurable process efficiency and cost savings.
Procurement definition
Procurement is the strategic process of sourcing and acquiring the goods and services that an organization needs to fulfill its business objectives. Unlike purchasing, which is often viewed as a transactional function focused on the act of buying, procurement encompasses a broader spectrum of activities. Read more about procurement vs purchasing. These activities include identifying business needs, conducting market research, evaluating suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships. The aim is not just to buy, but to ensure that purchases support the strategic goals of the organization, such as cost savings, innovation, quality improvement, and risk management.
The importance of procurement extends beyond the simple acquisition of goods and services. It plays a critical role in the overall financial health and operational efficiency of an organization. Effective procurement strategies can lead to significant cost savings by optimizing spend, leveraging supplier relationships for better terms, and reducing waste and inefficiencies. Furthermore, procurement is pivotal in ensuring the quality and reliability of the inputs into an organization’s operations, directly impacting the final product or service delivered to customers.
Procurement also plays a strategic role in supply chain management. By working closely with suppliers and integrating procurement strategies with supply chain operations, organizations can enhance their market responsiveness, improve supply chain resilience, and foster innovation. In today’s global economy, where supply chains are increasingly complex and exposed to various risks, the ability to manage procurement effectively can be a significant competitive advantage.
Another crucial aspect of procurement is its impact on sustainability and ethical sourcing. Organizations are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices, from environmental impact to labor practices of their suppliers. Strategic procurement enables organizations to enforce sustainability standards and ethical practices among their suppliers, aligning with corporate social responsibility goals and regulatory requirements.
The procurement process
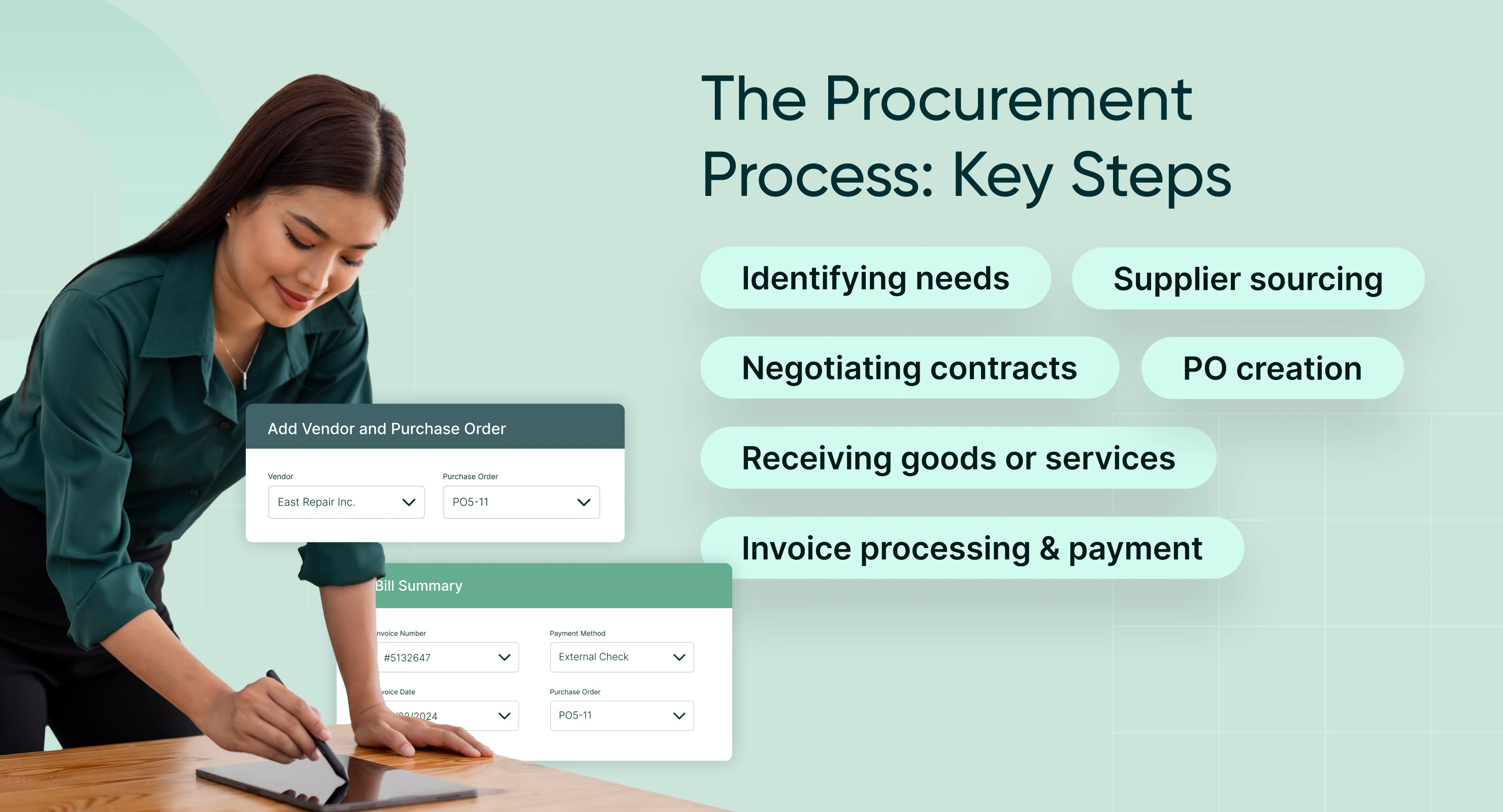
The procurement process is a systematic series of steps that organizations follow to ensure the efficient and effective acquisition of goods and services. This process is not just about making purchases but about ensuring these purchases align with the company’s strategic goals and objectives. Here’s a breakdown of the typical stages involved in the procurement process:
-
Need identification
-
Supplier research and selection
-
Tendering or request for proposal (RFP) process
-
Contract negotiation and award
-
Order management
-
Invoice approval and payment
-
Performance review and contract management
Effective procurement goes beyond the mere transactional aspect of buying goods and services. It involves strategic planning, thorough market research, careful supplier selection, and ongoing management of supplier relationships.
Want to dive deeper? We have written an article dedicated to the procurement process.
Types of procurement
Procurement activities can generally be categorized into two main types: direct and indirect procurement. Both play crucial roles in an organization’s operations, but they differ significantly in their purpose, processes, and impact on the business. Understanding these differences is key to developing effective procurement strategies.

Direct procurement
Direct procurement involves the acquisition of goods and services directly used in the production of a final product or service delivered to the end customer. This includes raw materials, components, and parts that are integral to manufacturing processes. For example, a car manufacturer procuring steel for car bodies or a construction company purchasing concrete for its projects.
The characteristics of direct procurement include:
-
Strategic importance:
Direct procurement is closely linked to the company’s core business activities and directly impacts product quality, manufacturing efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
-
Volume and value:
Purchases in direct procurement are often made in large volumes and are of significant value, given their direct impact on production.
-
Supplier relationships:
Establishing strong, long-term relationships with suppliers is critical in direct procurement to ensure reliability, quality, and supply chain continuity.
Indirect procurement
Indirect procurement, on the other hand, involves purchasing goods and services that support the organization’s operations but are not part of the final product or service offered to customers. This includes office supplies, maintenance services, software, and utilities.
The characteristics of indirect procurement include:
-
Operational necessity:
While not contributing directly to the production of the final product, these purchases are essential for the smooth operation of the business.
-
Varied stakeholders:
Indirect procurement often involves a wider range of stakeholders within the organization, from IT and facilities management to human resources and finance.
-
Cost management:
Effective management of indirect procurement can lead to significant cost savings, as these purchases, while smaller in value individually, can add up to a substantial portion of a company’s spend.
Want to know more? Check out this article: Direct vs. indirect procurement
Procurement management
Procurement management refers to the strategic approach to managing both direct and indirect procurement processes effectively. It encompasses the identification of needs, selection of suppliers, negotiation of contracts, and management of supplier relationships. Enhanced procurement management involves leveraging technology, data analytics, and market insights to optimize procurement activities, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
Procurement strategy
A procurement strategy outlines how an organization plans to manage and optimize its procurement activities. It is a comprehensive approach that considers various factors, including cost reduction, supplier management, risk mitigation, and the integration of technology. Developing a robust procurement strategy involves several key components:
-
Alignment with business goals
-
Market analysis and supplier selection
-
Cost management and efficiency
-
Risk management
-
Technology and innovation
-
Sustainability and ethical sourcing
-
Continuous improvement and adaptation
A well-defined procurement strategy enables organizations to manage their procurement activities more effectively, delivering significant value and supporting strategic objectives.
Want to know more? We have a deep dive article on procurement strategy.
Procurement vs. purchasing
Understanding the difference between procurement and purchasing is crucial for organizations aiming to optimize their supply chain and strategic sourcing efforts. While both functions are integral to acquiring goods and services, they operate at different stages of the acquisition process and involve varying degrees of strategy and planning.
What is purchasing?
Purchasing is the transactional function of buying goods and services. It involves activities such as placing orders, receiving goods, and processing payments. Purchasing is focused on the short-term goals of acquiring the needed inputs at the best possible price and terms. The primary objectives of purchasing include:
-
Ensuring the timely acquisition of goods and services
-
Minimizing costs through effective negotiation and vendor selection
-
Managing the ordering process and payment transactions efficiently
Purchasing is often seen as a subset of procurement, dealing specifically with the transactional, day-to-day activities that fulfill the strategic plans laid out by procurement.
What is procurement?
Procurement encompasses a broader scope than purchasing. It is a strategic function that involves planning, sourcing, negotiating, and managing goods and services that an organization needs to fulfill its business objectives. Procurement aims to build strong relationships with suppliers, manage risks, and achieve long-term benefits for the organization.
Key aspects of procurement include:
-
Identifying the needs of the organization and specifying requirements for goods and services
-
Conducting market research and supplier evaluation to find the best sources of supply
-
Negotiating contracts and terms to ensure value for money, quality, and reliability
-
Managing supplier relationships to ensure continuous improvement and adherence to contracts
-
Incorporating sustainability and ethical considerations into the sourcing process
Procurement is strategic, focusing on long-term goals such as cost savings, supplier performance, risk management, and the alignment of purchasing activities with the company’s overall strategy.
The strategic link
The difference between procurement and purchasing highlights the evolution of the procurement function from a purely transactional role to a strategic partner in the business. Effective procurement strategies go beyond the act of buying to ensure that every purchasing decision supports the broader business objectives, including sustainability, innovation, and market competitiveness.
Still have questions? We have an entire article dedicated to procurement vs. purchasing.
Procurement and supply chain management
Procurement and supply chain management are closely intertwined functions within an organization, each playing a vital role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services from suppliers to the end customer. While procurement focuses on the strategic process of sourcing and acquiring goods and services, supply chain management encompasses a broader spectrum of activities aimed at optimizing the end-to-end process of delivering products to the market.
Here’s how procurement fits into the larger context of supply chain management:
-
Strategic sourcing and procurement
-
Supplier relationship management
-
Risk management
-
Integration and optimization
-
Leveraging technology
Procurement is not just a function that operates in isolation; it is an integral part of the supply chain ecosystem. By aligning procurement strategies with supply chain management goals, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and competitive advantage.
Read more about the integration between procurement and supply chain management.
The impact of technology on procurement
The advent of digital technologies has revolutionized the procurement landscape, enabling organizations to automate routine tasks, harness the power of data for strategic decision-making, and enhance supplier collaboration. Among these technologies, procurement software and artificial intelligence stand out for their potential to significantly transform procurement practices.
Procurement automation
Procurement automation refers to the use of software and tools to digitize and streamline procurement processes, from supplier selection and contract management to purchase order processing and invoice approval.
Automation brings numerous benefits to the procurement function, including:
-
Efficiency gains:
By automating routine tasks, organizations can reduce the time and resources spent on transactional activities, allowing procurement teams to focus on strategic aspects such as supplier relationship management and strategic sourcing.
-
Error reduction:
Automation minimizes the risk of human error in procurement processes, leading to more accurate order processing, invoicing, and record-keeping.
-
Improved compliance:
Procurement software can enforce procurement policies and procedures, ensuring that all purchases comply with organizational standards and regulatory requirements.
Enhanced visibility: Automation tools provide real-time insights into procurement activities, spending patterns, and supplier performance, enabling better control and management of the procurement function.
Artificial intelligence in procurement
Artificial intelligence is taking procurement automation to the next level by enabling more intelligent and predictive capabilities. AI applications in procurement include:
-
Predictive analytics:
AI can analyze vast amounts of data to forecast future trends in prices, demand, and supplier performance, helping procurement teams make more informed decisions.
-
Supplier selection and evaluation:
AI algorithms can assess supplier capabilities, reliability, and risk factors more efficiently than traditional methods, improving the accuracy and speed of supplier selection.
-
Contract analysis:
AI-powered tools can review and analyze contracts, identifying key terms, compliance issues, and opportunities for renegotiation.
-
Chatbots and virtual assistants:
AI-driven chatbots and assistants can streamline interactions with suppliers and internal stakeholders, providing quick responses to inquiries and facilitating smoother communication.
The integration of procurement software and artificial intelligence is not just about efficiency; it’s about transforming procurement into a strategic function that drives innovation, reduces risk, and delivers value to the organization. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly unlock new possibilities for procurement professionals to contribute to their organizations’ strategic goals.
Future trends and technologies in procurement
As we look to the future, the procurement function is set to undergo even more significant transformations, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in global business practices. Here are some key trends and technologies that are shaping the future of procurement:
-
Advanced analytics and big data
The increasing availability of big data and advanced analytics tools is enabling procurement teams to gain deeper insights into spending patterns, supplier performance, and market trends. These insights can drive more informed strategic decisions, from supplier selection to contract negotiation.
-
Blockchain for transparency and efficiency
Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize procurement by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency in transactions. By enabling secure, real-time sharing of transaction records between buyers and suppliers, blockchain can reduce fraud, improve contract compliance, and streamline payment processes.
-
Integration of AI and machine learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to become more deeply integrated into procurement processes, automating complex decision-making tasks such as supplier evaluation, risk assessment, and demand forecasting. This integration will not only improve efficiency but also enhance the strategic capabilities of procurement functions.
-
Sustainable procurement practices
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in procurement, with organizations increasingly prioritizing environmental and social factors in their purchasing decisions. Future procurement practices will involve more rigorous sustainability assessments, sustainable supplier development programs, and greater use of eco-friendly products and services.
-
Collaborative supplier relationships
The future of procurement lies in building more collaborative and strategic relationships with suppliers. This involves moving beyond transactional interactions to develop partnerships that foster innovation, flexibility, and mutual growth. Technology will play a key role in facilitating these collaborative ecosystems.
-
Digital procurement platforms
The rise of digital procurement platforms is streamlining the procurement process, offering end-to-end solutions that cover everything from supplier discovery and e-tendering to contract management and analytics. These platforms are making procurement more accessible, efficient, and scalable, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
-
Tailored procurement strategies
As businesses become more dynamic, there’s a growing need for procurement strategies that are tailored to specific industry challenges, business models, and market conditions. Customized procurement approaches, supported by data analytics and AI, will enable organizations to optimize their procurement activities more effectively.
Procurement FAQs
So what?
As you can see, the world of procurement has a lot of moving pieces.
Everything from supplier management to risk management to leveraging AI technology are all factors that will impact how effective and efficient your procurement strategy will be.
Now that you understand the full scope of the procurement process and its significance to the operations and bottom line of a business, you are ready to choose your procurement software and implement a comprehensive procurement strategy.
By considering these factors and the insights provided in this article, you can start making informed decisions and select the software that best fits your requirements. Procurify is here to assist you in your procurement journey.
Book a demo today to experience how our procure-to-pay software simplifies the procurement process, enabling full control and visibility over your spend.

2025 Procurement Benchmark Report
Powered by $20B+ in proprietary data you won’t find anywhere else.





